Friday, November 29, 2013
Monday, November 25, 2013
6-Evaluation
Once the new system has been implemented and is in full use, the system should be evaluated (this means that we take a long, critical look at it).
The purpose of an evaluation is to assess the system to see if it does what it was supposed to do, that it is working well, and that everyone is happy with it
The purpose of an evaluation is to assess the system to see if it does what it was supposed to do, that it is working well, and that everyone is happy with it
.
How is a System Evaluated?
The systems analyst will use a number of techniques to evaluate the system...
Check against the
Requirements Specification
Requirements Specification
If you remember, earlier on in the Systems Analysis, the old system was analysed, and a checklist of targets was drawn up for the new system.
This list was called the Requirements Specification.
The systems analyst will use this document to check the new system. Going through therequirements one-by-one the analyst will check if they have been met.
This list was called the Requirements Specification.
The systems analyst will use this document to check the new system. Going through therequirements one-by-one the analyst will check if they have been met.

Check the
Users' Responses
Users' Responses
It is essential to get feedback from the usersof the system...
- Do they like it?
- Does it make their work easier?
- What, if anything, could be improved?
- Questionnaires
- Interviews
- Observations

5- Documentation
There are two types of documentation that should be produced when creating a new system:
- User documentation
- Technical documentation
Testing
Documentation
Implementation
User Documentation
The user documentation is intended to help the users of the system.
The users are usually non-technical people, who don't need to know how the system works. They just need to know how to use it.
User documentation usually includes:
The users are usually non-technical people, who don't need to know how the system works. They just need to know how to use it.
User documentation usually includes:
- List of minimum hardware and software required to use the system
- How to install the system
- How to start / stop the system
- How to use the features of the system
- Screenshots showing the system in typical use
- Example inputs and outputs
- Explanations of any error messages that might be shown
- A troubleshooting guide
The technical documentation is intended to help the maintainers of the system (the people who need to keep the system running smoothly, fix problems, etc.)
The maintainers are usually technical people, who need to know exactlyhow the system works.
Technical documentation usually includes:
The maintainers are usually technical people, who need to know exactlyhow the system works.
Technical documentation usually includes:
- Details of the hardware and software required for the system
- Details of data structures (data types, field names, etc.)
- Details of expected inputs
- Details of validation checks
- Details of how data is processed
- Diagrams showing how data moves through the system
- Flowcharts describing how the system works
3- Testing and development
A test plan is usually written whilst the system is being developed. The test plan will contain details of every single thing that needs to be tested.
A typical test would contain:
- Details of what is being tested
- The test data to use
- What is expected to happen when the test is performed
When is the System Tested?
Testing is normally done in two stages...
The first phase of testing is done by the designers and engineers who created the system, usually before the system is delivered to the customer.
The test data that is used in this first phase is similar to data that would be used by the actual customer.
The second phase of testing is done after the system has been delivered and installed with the customer.
The data used in the second phase is usually 'live' data - data that is actually part of the customer's business / organisation.What Happens if the System Fails Some Tests?
The first phase of testing is done by the designers and engineers who created the system, usually before the system is delivered to the customer.
The test data that is used in this first phase is similar to data that would be used by the actual customer.
The second phase of testing is done after the system has been delivered and installed with the customer.
The data used in the second phase is usually 'live' data - data that is actually part of the customer's business / organisation.What Happens if the System Fails Some Tests?
The whole point of testing is to try and find areas that don't work as they should, or areas that can be improved.
If any failures are found, the systems analyst goes back and does some further research, analysis and design to fix these areas.
If any failures are found, the systems analyst goes back and does some further research, analysis and design to fix these areas.
2- Design
Using the list of requirements, the systems analyst now has to design the new system.
In most cases the new system will be computer-based. The ease with which computers can communicate and process data means that are usually the best tool for the job.
In most cases the new system will be computer-based. The ease with which computers can communicate and process data means that are usually the best tool for the job.
Analysis
Design
Testing
Designing the System Inputs
To get data into a system is a two-part process:
- Data must first be ‘captured’ (collected in a way that then makes it easy to input)
- Data must be input into the computer
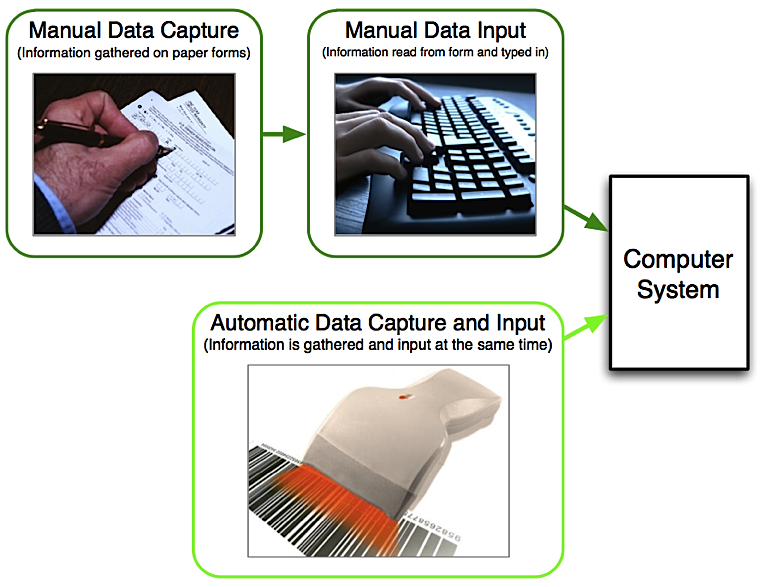
System
analysis
Systems Analysis is, as the name states, the analysis of systems!
The systems that we are talking about are the systems within organisations and businesses - systems of communication, financial systems, manufacturing systems, etc. - basically the systems that make the organisation or business work.
A person who analyses systems is known as a Systems Analyst.
Often systems analysts are employed by organisations of businesses to help them improve their systems and so become more efficient, and for businesses, more profitable.
A systems analyst would generally perform the following steps in the order shown...
The systems that we are talking about are the systems within organisations and businesses - systems of communication, financial systems, manufacturing systems, etc. - basically the systems that make the organisation or business work.
A person who analyses systems is known as a Systems Analyst.
Often systems analysts are employed by organisations of businesses to help them improve their systems and so become more efficient, and for businesses, more profitable.
A systems analyst would generally perform the following steps in the order shown...
Production
Creating the new system from the design. (Note: details of this stage are not required for IGCSE)
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)





